Subject : Rajkot Gaming Zone Fire
Place of Incident: TRP Game Zone at Rajkot, Gujarat
Date: May 25, 2024
Time: At around 4.40 pm
Casualties : 28 victims (25 identified so far), including 4 children under 12 years old (source: Hindustan Times report)
Occupancy Type: Gaming zone/ Amusement (Group D Assembly building according to NBC part 4)
Introduction:
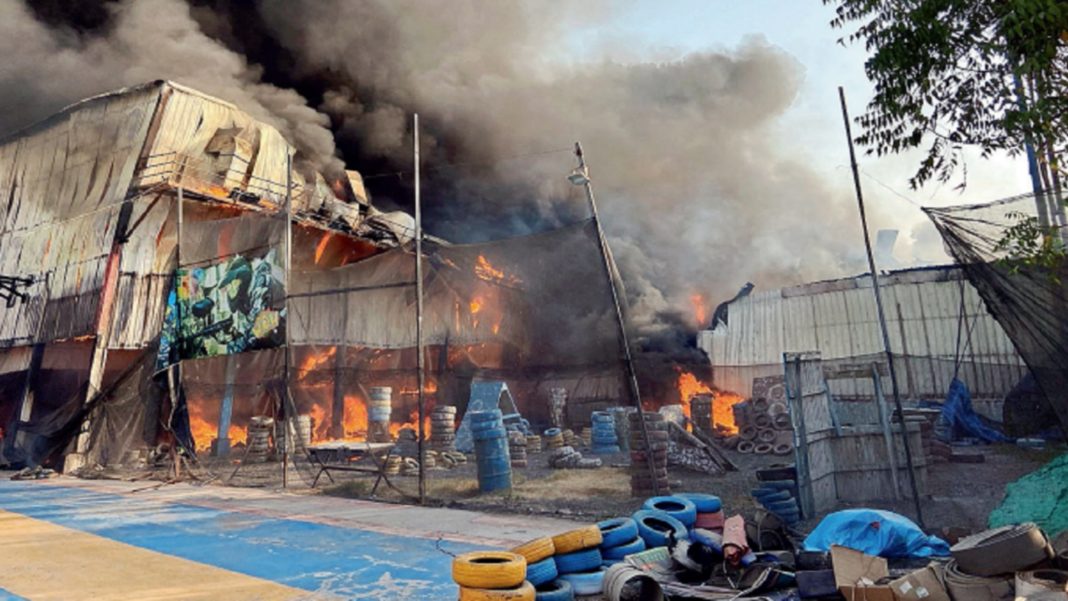
On May 25, 2024, a tragic fire incident occurred at the TRP Game Zone in Rajkot, Gujarat. The fire, which broke out in the gaming zone premises, resulted in 28 casualties, among the victims, at least four were children under the age of 12. The TRP Game Zone is a popular amusement location. Gujarat High Court has called this a “man made disaster” taking ‘suo motu cognisance’ and the Police have lodged a FIR against six persons.
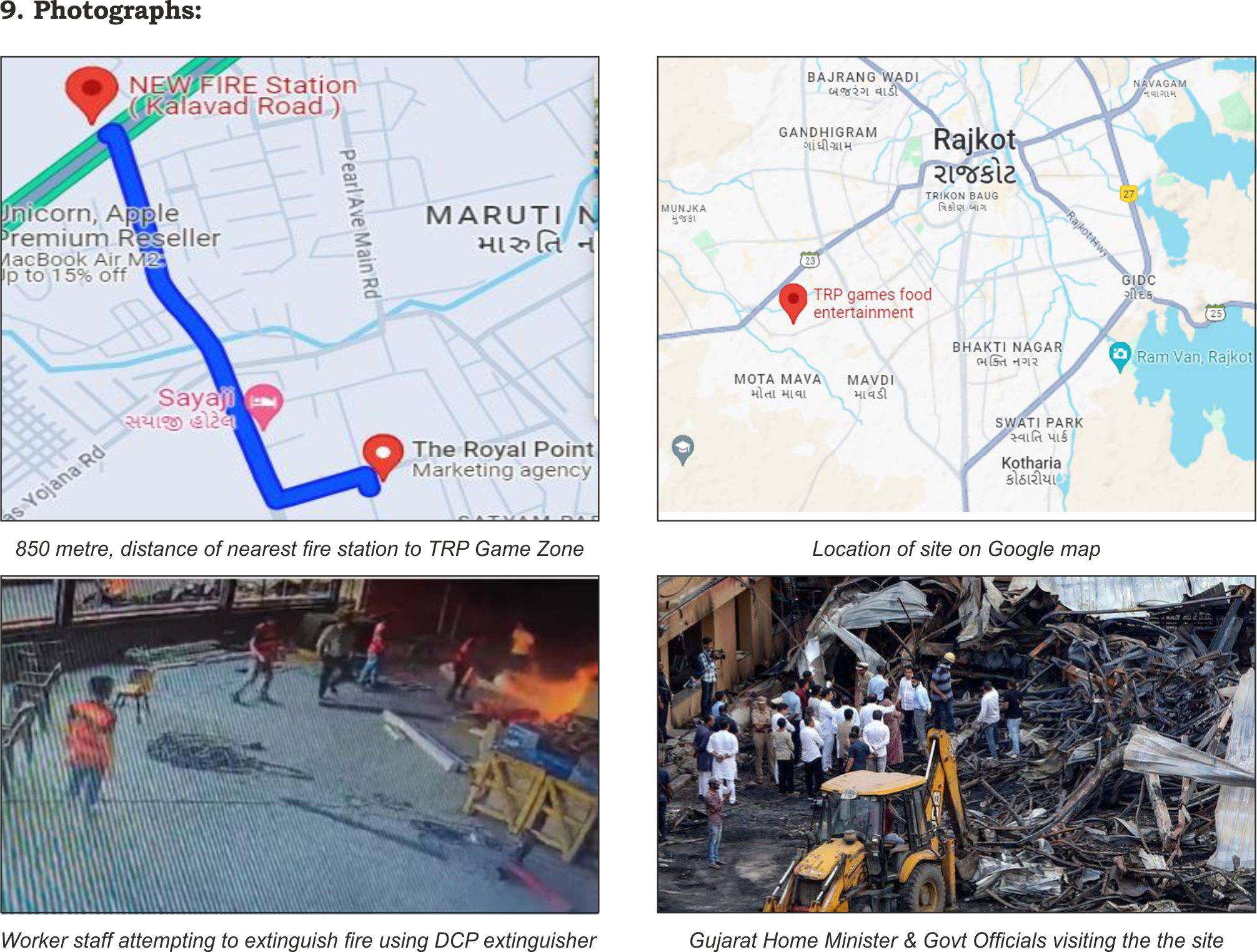
The origin of the fire was traced to welding work being carried out on the premises. Sparks from the welding flew into a pile of flammable sheet material stored nearby, igniting a blaze. Despite the workers immediate attempts to extinguish the fire, it quickly grew, leading to the devastating outcome.
Fire Fighting and Rescue Operation:
(Source : ThePrint)
The exact timeline of the firefighting and rescue operation at the Rajkot TRP Game Zone fire remains unclear due to conflicting accounts. Here’s a breakdown of the available information:
2.1. Possible Ignition Time:
Eyewitness reports suggest smoke was visible as early as 4:45 pm which led to panic in nearby colony around that time. One witness claims a call about the fire was made at 5 pm.
2.2. Fire Department Response:
Official records from the fire department state their first vehicle left the station at 5:43 pm and arrived at the scene by 5:47 pm. This contradicts the police FIR, which claims the first call reached them at 5:47 pm.
2.3. Fire Progression and Delays:
By the time some eyewitnesses arrived around 5 pm, the fire was already established. One witness claims they waited at least 45 minutes before a fire truck arrived. Another witness suggests the fire spread rapidly within 10 minutes, leading to a structural collapse.
2.4. Uncertainties and Allegations:
The exact cause of the initial delay in fire department response remains unclear. There are allegations that staff did not evacuate patrons in a timely manner. Some reports suggest this wasn’t the first fire incident at the game zone, raising questions about fire safety measures.
2.5. Impact:
The delayed response and potential evacuation issues likely contributed to the tragic outcome of the fire.
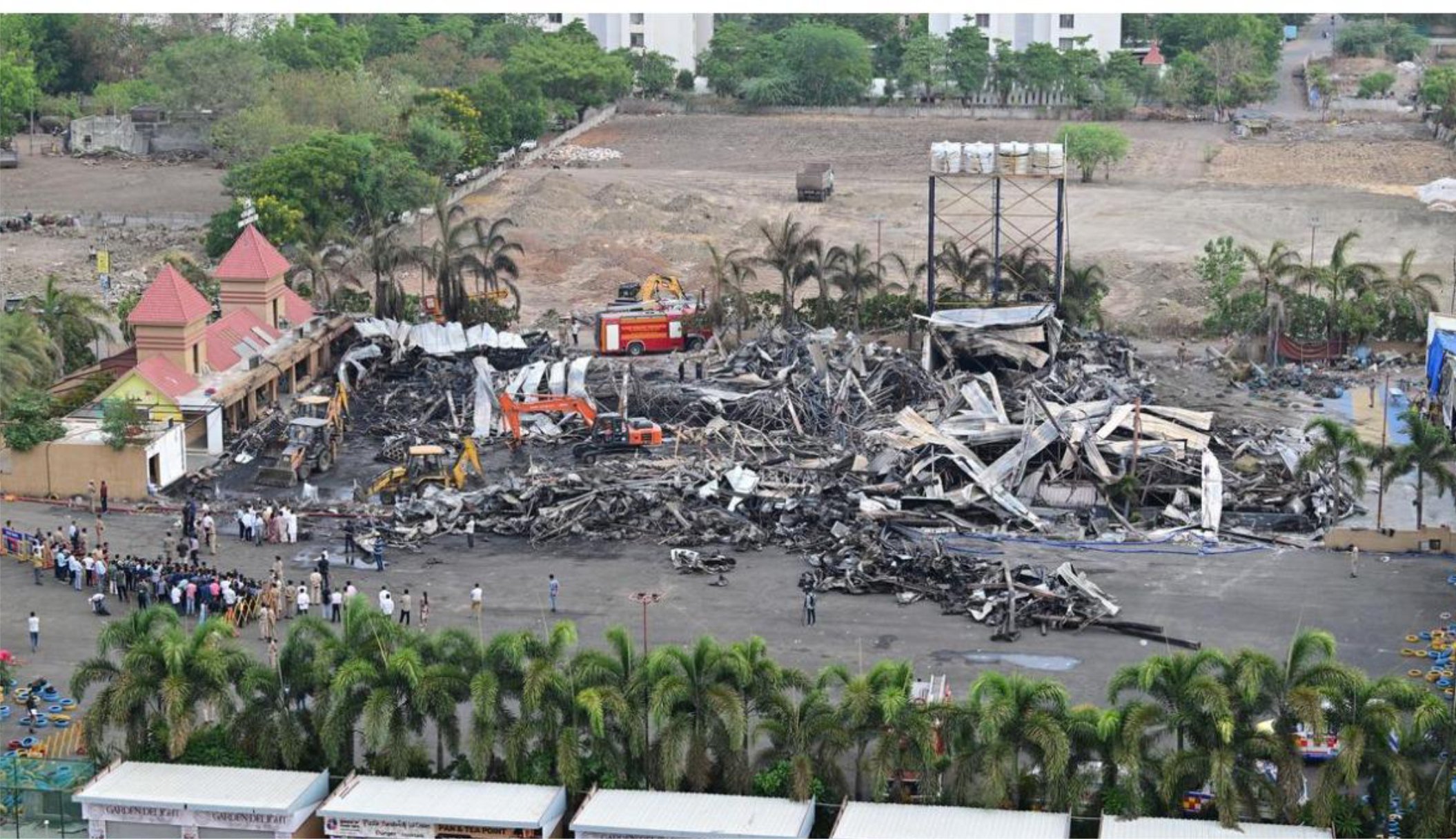
The fire at the TRP Game Zone in Rajkot presented significant challenges for firefighters.
- Multiple Fire Tenders Deployed: News reports indicate numerous fire tenders rushed to the scene upon receiving news of the blaze.
- Difficulties in Containing the Fire: The reports mentioned difficulties in extinguishing the fire due to factors like:
- Temporary Building Structure: The fire’s intensity might have been amplified by the building’s temporary construction, potentially collapsing and hindering access.
Wind Velocity: Strong winds could have exacerbated the flames’ spread.
2.6. Rescue Operations:
Details regarding the rescue efforts might be limited due to the fire’s intensity. However, firefighters likely focused on evacuating those trapped inside the burning building.
Casualties:
According to a report by The Indian Express, 25 out of the 27 victims have been identified so far. Among the total victims, at least four were children under the age of 12, but only two of these children have been identified so far, according to the report.
The police reported that three additional people were injured in the incident and were transported to a nearby hospital for treatment. “Their condition is stable,” stated Additional Commissioner of Police (ACP) Vinayak Patel to PTI.
The bodies were severely charred, making recognition impossible. DNA samples from the bodies and from the victims’ relatives have been collected to assist in identifying the deceased.
Observations:
- Huge piles of flammable foam sheets (Polyurethane) was stacked at a location
- The welding work was ongoing right above those foam sheets without considering any safety precautions or mindful examination of the scene
- Precautionary fire equipments for construction were not present
- Absence of Fire Alarm System & Fire Protection System
- Wrapped and Non-functional fire equipments were in upper floor, so the travel distance and time taken for the response increased
- Only one exit/entry present at the Game Zone
- 3000 litres of diesel stored onsite for Go-Kart
- The temporary structure made of tin sheets did not have the NOC (Fire Dept & Municipality) and still public gathering was conducted
- Due to collapse of temporary structure, people were trapped inside endangering life, also made the rescue operation difficult
- The tyres (gaming props) obstructed the entry of fire vehicle, eventually delayed the fire fighting operation
Probable Causes:
A nearby thermocol sheet caught fire from a welding spark, quickly spreading to the entire 3,000 square meter game zone area. The site contained fuel, tires, fiberglass shades, and thermocol sheet partitions, which were intended for go-karting at the gaming zone.
The structure was made entirely of fabrication, covered with tin sheets, and contained open wiring, AC pipes, iron angles, and galvanized tin sheets. Additionally, the presence of fire-prone tarpaulin contributed to the rapid spread of the fire.
The use of first aid fire extinguishers was also not timely, as the fire grew past the incipient stage, due to this they proved ineffective upon application. Limited and obstructed exits affected the evacuation costing life of public
Legal Actions & Government’s Response:
6.1. Arrests and Charges:
Six individuals have been accused in connection with the fire, including the gaming zone owner, Dhaval Thakkar. Three arrests have been made so far, with Dhaval Thakkar being the most recent.
A court in Rajkot remanded three arrested suspects to 14-day police custody. All six accused face charges under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) for culpable homicide, attempt to commit culpable homicide, causing hurt, and abetting an offense.
6.2. Government Response:
The Gujarat government suspended seven officials for negligence in allowing the game
zone to operate without proper approvals. These include officials from the Rajkot Municipal Corporation, the Roads and Buildings department, and the police.
The Chief Minister ordered strict action against those responsible for the incident.
A Special Investigation Team (SIT) has been formed by the state government to investigate the fire. The Gujarat High Court took suo motu cognisance of the incident, calling it a “man-made disaster.”
Gujarat DGP Vikas Sahay has ordered the closure of all game zones in different cities of the state as a precautionary measure, and safety measures including those related to fire are being verified.
6.3. Financial Assistance:
The Gujarat government announced an ex gratia payment of Rs 4 lakh from the PM’s National Relief Fund to the kin of each deceased person.
The Central government also announced an ex gratia payment of Rs 2 lakh to the next of kin of each deceased person. The injured persons would be given Rs 50,000, the Prime Minister’s Office said on X.
Corrective Comments:
7.1. According to IS 8758: Fire Precautionary Measures In Construction of Temporary Structures And Pandals — Code of Practice[7]
7.2 General Recommendations:
Prevention:
- Acquiring legal permits/ NOC from the Municipal Corporation and the state fire department before starting operation and allowing public entry into the structure shall be compulsory.
- In case of welding or any other work involving a potential ignition source is on going it shall be monitored by the owner or the contractor at all times.
- Work of such nature shall not be done until the surrounding area is assessed and all the combustible/ flammable materials have been removed from the place and relocated to a safe distance.
- No construction or welding work should be carried out when the location is occupied by the general public.
- Ensure proper fire protection equipment has been installed and made functional before starting procurement of goods into the temporary structure and starting any construction or maintenance work.
- When doing work that involves a potential ignition source or risk of fire, functional first aid fire protection equipment must be kept in the vicinity.
- The structure must contain an adequate number of ingress and egress routes to facilitate safe and timely evacuation of occupants in case of an emergency.
- Proper signage for exit routes must be installed, so reduce panic and ensure safe egress of occupants during emergencies.
- Storage of flammable liquids above the allowable quantity according to National Building Code shall not be allowed.
- Regular inspection of the site must be done to ensure all flammable materials are stored properly and not accumulated in areas prone to fire hazards.
- The structure, even if temporary, shall have a fire detection and alarm system to immediately detect fire at the incipient stage.
- A public address system shall also be present in order to communicate the state of emergency and facilitate timely evacuation.
- The workers on site must be trained in the use of first aid fire fighting equipment.
- All the workers must be aware of potential hazards associated with the work being carried out and be trained to handle emergency situations efficiently.
- The route for the entry of fire fighting vehicles must be clear and must facilitate easy access to the site of accident, so that quick response can be made.
Conclusion:
The tragic fire at the TRP Game Zone in Rajkot, Gujarat, on May 25, 2024, which resulted in 28 casualties, underscores the critical need for stringent fire safety protocols and regulations, particularly in temporary structures. The incident was triggered by sparks from welding work igniting flammable foam sheets stored nearby, leading to a rapid and devastating blaze. The response from the fire department was delayed and hampered by the inadequate safety measures, contributing significantly to the high casualty rate.
Key observations reveal multiple lapses, including improper storage of flammable materials, lack of fire alarms, insufficient fire-fighting equipment, inadequate evacuation routes, and unauthorized structural modifications. Additionally, the presence of obstructive elements and insufficiently trained staff further complicated the rescue operations.
In the aftermath, legal actions were taken against six individuals, including the game zone owner, and the government suspended several officials for negligence. The Gujarat High Court termed the incident a “man-made disaster” and a Special Investigation Team (SIT) was formed to probe the fire. Moreover, financial assistance was announced for the victims’ families.
Foam sheets, typically made from flammable polyurethane or polyethylene, contain many C-H bonds. When heated, these bonds break, releasing volatile compounds that react with oxygen, quickly producing heat, flames, and combustion gases. The C-H bond, with a bond energy of about 413 kJ/mol, stores significant potential energy. When broken, it releases high energy, sustaining the fire.
Combustion of these materials releases toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, formaldehyde, and hydrogen cyanide, causing dizziness, headache, nausea, confusion, and loss of consciousness. High concentrations can be fatal within minutes, while prolonged exposure to lower concentrations can lead to chronic respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and neurological damage. These toxic gas releases likely contributed significantly to fatalities.
This incident highlights the dire consequences of neglecting fire safety standards and emphasizes the urgent need for comprehensive fire safety audits, stricter enforcement of regulations, and enhanced training for staff to prevent such tragedies in the future.
By Interns at IIT Gandhinagar:
Rachit Singh, Pooja Kathariya, Jerin Bejoy Joy Ponthakken